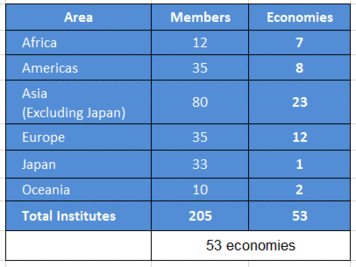
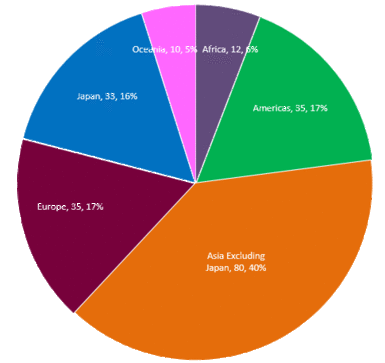
Members
The membership of GADRI is open to institutes with an aim to contribute to the advancement of disaster research, and those working in the field of disaster risk reduction. Various research institutions from around the world have joined GADRI among which are universities, networks, organizations in collaboration with UN agencies such as UNU, UNDRR, UNESCO, and others.
Our expectations from member institutions among others include:
- identify status of the current research gaps in their area of research to achieve disaster risk reduction in the real world;
- commitment and contribution to the goals of the Science and Technology Raodmap for the implementation of the Sendai Framework Agenda for 2030;
- development of new methodologies and technologies for data analyses, promotion of action data and encouragement of open data sharing, for research and risk reduction applications;
- self-evaluation of research achievements and sharing of knowledge during the GADRI biennial global summit sessions.
Currently, there is no fee required to become a member.
To view the list of members, visit the page for member institutions.
member institutions
Geographical distribution of members of GADRI - as of April 2020.
Institutes interested in joining GADRI should complete the membership and institute data forms, and submit these to the GADRI Secretariat (secretariat-gadri@dpri.kyoto-u.ac.jp).
Abu Dhabi - Rabdan Academy
 |
Rabdan AcademyAl Inshirah Contact Person: Dr. Matthew Ellis |
| Outline Rabdan Academy is a government-owned world-class education institution established to coordinate and enhance learning outcomes for organisations and individuals in the Safety, Security, Defence, Emergency Preparedness and Crisis Management (SSDEC) Sectors. The Academy was officially established under Law No. 7 for 2013, issued by the late Sheikh Khalifa bin Zayed Al Nahyan and is accredited by the UAE's Commission for Academic Accreditation (CAA) of the Ministry of Education. The Academy is the first higher education institution in the world specialised in the SSDEC domain that achieves top '5 star' ratings in the 2 categories of Teaching and Employability under the QS Stars University Rating System. As a unique institution, the Academy provides learning in a dual approach, combining academic and vocational education in one place, whilst recognising prior learning and experience and providing accredited and transferable credit from course to course and job to job. [detail] --> |
|
 |
Faculty of Civil Engineering, University of Sciences and Technology Houari BoumedieneAlger Contact Person: Prof. Djillali Benouar |
| Outline Located 15km outside of the capital Algiers, the University of Sciences and Technology Houari Boumediene (USTHB) is a modern university that focuses Computing, Pure and Applied Mathematics, Physics, Chemistry, Biology, Geology, Civil Engineering, Electronics, Information Technology, Process Engineering, and Mechanical Engineering. It has developed strong networks and undertaken many research collaborations with western universities, especially in France. USTHB is home to the Built Environment Research Laboratory (LBE), founded in 2000. The LBE operates in the context of numerous national and international projects, with a specific research focus on Earthquake Engineering, Structural Dynamics, Engineering Seismology, Building Materials, Disaster Management, Vulnerability Evaluation and Preservation of Cultural Heritage. The mission of the LBE unit is to conduct research on earthquake risk reduction, building the capacity of practitioners to address seismic risk and serve as a source of consult for the Algerian government and abroad. Currently, the LBE comprises four teams and incorporates 25 researchers (from within USTHB and outside), six with PhDs. The LBE is also active in lobbying for a greater focus on disaster risk reduction initiatives in the country and abroad. Other activities of the unit include conducting several workshops on assessing seismic vulnerability in several African countries and research on state of risk reduction for UNICEF. [detail] --> |
|
 |
Geography Institute "Romualdo Ardissone" - University of Buenos AiresBuenos Aires Contact Person: Prof. Jorge Blanco |
| Outline The Program of Investigations in Natural Resources and Environment (PIRNA) works since 1988 in the Institute of Geography of the Faculty of Philosophy and Letters of the University of Buenos Aires. Its objective is to generate knowledge and train researchers in the problem of the use and management of natural resources and the environment, with an emphasis on aspects related to territorial configurations. The central issue addressed is the study of social vulnerability as a dimension of environmental risk in relation to hazards of various kinds. For this purpose, qualitative and quantitative methodologies for diagnosis and analysis have been developed, including participatory interaction with social actors. In recent years, this knowledge has been applied to the problem of adaptation related to climate dynamics, both in national and international research projects, and in the transfer to the public and non-governmental sectors. The PIRNA promotes lines of research related to environmental risk, particularly related to catastrophes of hydroclimatic origin. In relation to our research, the topics that would be interesting to deepen can be the following:
|
|
 |
Fenner School of Environment and Society
|
| Outline There are few places in the world where economists, hydrologists, historians, ecologists, foresters, geographers and climatologists all work together seeking solutions to some of contemporary society's most significant challenges. The Australian National University's Fenner School of Environment and Society is one such place and provides a forum for the rigorous exploration of diverse ideas, perspectives, and methods of identifying and solving problems at the interface of the natural and social sciences, including the humanities, as they apply to the environment and sustainability. Fenner offers expert perspectives on complex environmental and sustainable development challenges, drawing on decades of quality empirical and applied research. Research focuses on understanding environmental changes across a range of scales in time and place, enabling the school to provide past, present and future narratives to guide science, policy and management. Of particular importance to us is our capacity to encourage sound policy and governance outcomes that support sustainability. |
|
Australia - HEDMS-Charles Darwin University
 |
Humanitarian, Emergency and Disaster Management Studies
|
| Outline The Humanitarian, Emergency and Disaster Management Studies (HEDM) program at the Charles Darwin University (CDU) delivers advanced, globally competitive knowledge and practical skills to students from a wide range of professional and academic backgrounds. The program is situated at the door-step of the Asia-Pacific, the most disaster-prone region in the world. Through our degree programs and research, students learn how to approach disaster, emergency and community risks holistically. Teaching is informed by CDU's strong relationships with nationally and internationally respected industry and research partners. Interactive lectures are delivered by some of the world's leading experts in the discipline. Most of the courses are available in-campus and online. HEDM offers an interdisciplinary research program that deals with human dimensions of natural hazards, disaster and environmental risks and climate change adaptation. The potential research supervisors are world-class scholars in their field of research. Higher Degree by Research (HDR) at the Charles Darwin University covers the degrees of Masters by Research (MRes) and Doctor of Philosophy (PhD). HDR students engage in a supervised research project that demonstrates their ability to make a contribution to knowledge in a chosen field of study. [detail] --> |
|
 |
Centre for Disaster Studies
|
| Outline The Centre for Disaster Studies is a multi-disciplinary research unit within the College of Science and Engineering at James Cook University. The Centre has acted as the university's face to the public and the professionals in the Emergency Management and Meteorology fields, city councils and other researchers since its establishment in 1979. Members have extensive research expertise, field work experience and professional teaching capacity in community based disaster management (all hazards). Academic research members have a strong foundation in the following research areas (both domestic and international): - Integrated disaster risk reduction and climate change adaptation - Land use planning for disaster risk reduction (DRR) and climate change - Building resilience in the built, natural and social environment - Tourism crisis and disaster management - Vulnerability and capacity assessment (community mapping for DRR and recovery) - Social network analysis for disaster governance, risk reduction and resilience - Post disaster assessment for response and recovery - Sustainable development/redevelopment and livelihoods Affiliate members of the Centre also conduct relevant research in the fields of engineering, public health, nursing, journalism/media, psychology, education, anthropology, human geography and the broader social sciences. The Centre has extensive experience in the translation of research and science into effective policy recommendations and action. Full reports and publications available at : [detail] --> |
|
Australia-RMIT-Melbourne University
 |
Humanitarian Engineering Lab
|
| Outline RMIT University (officially the Royal Melbourne Institute of Technology), is a public research university in Melbourne, Australia. It is a global university with campuses in Australia, Vietnam and Spain. It offers a number of programs through partners in Singapore, Hong Kong, mainland China, Indonesia, Sri Lanka, India, Belgium, Germany, Austria and the Netherlands. It collaborates with communities and universities in the Asia-Pacific and other regions through the Disaster Research Network. RMIT's Disaster Research Network addresses the increasing need for research, innovation, and partnership to support disaster prevention, preparedness, response, and recovery in Australia and internationally. Drawing together over 80 researchers from a broad range of disciplines, the RMIT Disaster Research Network takes a multi-disciplinary approach to disaster research, working together with practitioners and communities to strengthen resilience and research impact. The Network provides our partners with easy access to research expertise and opportunities to collaborate. The Network also enables a coordinated and timely response to calls for research capability and facilitates industry-academia events. Affiliate members of the Centre also conduct relevant research in the fields of engineering, public health, nursing, journalism/media, psychology, education, anthropology, human geography and the broader social sciences. The Centre has extensive experience in the translation of research and science into effective policy recommendations and action. Full reports and publications available at : [detail] --> |
|
 |
Centre for Infrastructure Performance and Reliability (CIPAR)
|
| Outline The Centre for Infrastructure Performance and Reliability (CIPAR) is at the international forefront in assessing the reliability, safety, durability and management of buildings, bridges, pipelines, aviation, and other infrastructure systems. The pioneering research at CIPAR includes risk and reliability assessment, corrosion of infrastructure, and structural masonry. The Centre for Infrastructure Performance and Reliability (CIPAR) comprises the following areas of international research strength:
[detail] --> |
|
 |
GeoQuEST
|
| Outline The GeoQuEST Research Centre represents an interdisciplinary team from the Faculty of Science, Medicine and Health and the Faculty of Engineering and Information Sciences that have a focus on environmental and climate change research under the overall theme of Earth System Science and Technology. The centre brings together outstanding researchers studying the atmosphere, earth and water within the broad disciplines of geography, geology, environmental science and environmental engineering who share interests in environmental processes and climate change. [detail |
|
 |
Sustainability Research Centre
|
| Outline While USC was initially established as primarily a regional teaching university for undergraduates, it is now evolving into a targeted research university. The recent appointment of Professor Roland De Marco as USC's first Pro Vice-Chancellor of Research, underlined the university's commitment to supporting excellence in research. Three Research Centres now exist as focal points at USC: GeneCology Research Centre; Forest Industries Research Centre; and Sustainability Research Centre. Additionally, several other research clusters or themes have developed and new ones are emerging. Through these focal points, USC maintains research collaborations worldwide with a strong emphasis in the Asian-Pacific region. USC has recently enhanced its research profile through the recruitment of outstanding researchers and up-to-date infrastructure. The Sustainability Research Centre (SRC) was formalised as one of the University of the Sunshine Coast's flagship research concentrations in September 2007. In 2012 the SRC was also designated as a Tier 1 Research Centre, one of only three in the university. Within the past year, the SRC has made two critical research-based hires in geosciences (Professors Patrick Nunn and Roy C. Sidle) to increase its visibility and profile in biophysical sciences to complement the strong faculty counterpart in social sciences. The SRC has the capacity to attract top-level Honours students from various faculties and support post graduate students as well as Research Fellows. The SRC offer both undergraduate majors and minors in Sustainability and a Ph.D. by research in Sustainability. The core focus of the sustainability educational programs aligns with the social, behavioural, biophysical, and economic sciences. In addressing concerns of society and the environment, this important transdisciplinary research area offers a broad spectrum of opportunity.
[detail] --> |
|
 |
Queensland University of TechnologyBrisbane Contact Person: Prof. Ashantha Goonetilleke |
| Outline We are a team of academics who are actively engaged in research, teaching, and professional service across sub-disciplines of civil engineering. We have strong connections to the community of practising civil engineers, as well as leadership roles within the international academic community. Our researchers are involved in cutting-edge research programs, topics and projects across all of our sub-disciplines. Our research has made significant contributions to QUT's Excellence in Research for Australia (ERA) ratings. We received a 4 (above world standard) in environmental engineering, and a 3 (at world standard) for civil engineering. [detail] -->ERA (Excellence in Research for Australia) |
|
Australia-HADRI, Western Sydney University
Humanitarian and Development Research Initiative, Western Sydney UniversityPenrith, NSW Contact Person: Prof. Nichole Georgeou |
|
| Outline Western's School of Social Sciences and Psychology is home to expertise in disaster preparedness, response and management through its Humanitarian and Development Research Initiative (HADRI). HADRI research in this area examines public policy, international standards and scholarly research within the disaster management sector. The DRM theme has a particular focus on ethics and accountability, specifically the factors that govern their translation into organisational philosophies and implementation as operational outcomes achieved with affected communities. DRM also informs disaster epidemiology work within the HADRI team, including population health and mental health effects of disasters and both the research and policy frameworks which support effective linking of relief, rehabilitation and development (LRRD) programs. [detail] --> |
|
Austrian Institute of Technology (AIT)Vienna |
|
| Outline The AIT Austrian Institute of Technology is Austria's largest research and technology organisation. Among the European research institutes, AIT is a specialist in the key infrastructure issues of the future. As an Ingenious Partner to industry and public institutions, AIT is already researching and developing the technologies, methods and tools of tomorrow ‑ paving the way for the innovations of the day after tomorrow. The AIT Austrian Institute of Technology takes a leading position in the Austrian innovation system and a key role in Europe as the RTO focusing on the key infrastructure topics of the future. AIT provides research and technological development to realize basic innovations for the next generation of infrastructure related technologies in the fields of Energy, Mobility Systems, Low-Emission Transport, Health & Bioresources, Digital Safety & Security, Vision, Automation & Control and Technology Experience. These technological research areas are supplemented by the competence in the area of Innovation Systems & Policy. As a national and international network node at the interface of science and industry AIT enables innovation through its scientific-technological expertise, market experience, tight customer relationships and high-quality research infrastructure. An in-depth understanding of the challenges of crisis and disaster situations represents an essential prerequisite in order to protect the citizens, the environment as well as public and private infrastructures. With the advent of new Information and Communication Technologies (ICT) in the last decades, the domain of Crisis and Disaster Management (CDM) has gained the opportunity to greatly increase the efficiency and efficacy of its operations based on the real-time exchange and management of the relevant information. AIT's CDM group in the Center for Digital Safety & Security has in recent years made substantial contributions to the evolution of ICT paradigms and solutions for crisis and disaster management both on the Austrian national and at the international level. AIT's CDM activities and its portfolio of solutions is comprised of the following three areas:
[detail] --> |
|
Disaster Competence Network Austria (DCNA)Vienna |
|
|
Outline DCNA is strengthening security and disaster research by:
Achievements:
[detail] --> |
|
 |
International Institute for Applied Systems Analysis (IIASA)Laxenburg |
| Outline The International Institute for Applied Systems Analysis is a scientific research institute located in Laxenburg, near Vienna, Austria. Founded in 1972, the International Institute for Applied Systems Analysis (IIASA) conducts policy-oriented research into problems of a global nature that are too large or too complex to be solved by a single country or academic discipline. IIASA is sponsored by its National Member Organizationsin Africa, Asia, Europe, Oceania and the Americas. Its research is independent and completely unconstrained by political or national self-interest. [detail] --> |
|
 |
Institute of Water and Flood Management (IWFM)
|
| Outline Bangladesh is predominantly a floodplain country where water is key to socio-economic development and sustainability of the eco-system. Flood, drought, cyclone, river erosion, siltation, and water scarcity in dry season have made water management a challenging task. The gradual degradation of the environment due to human interventions is adding further complexities to water management. To address these issues, the Institute of Flood Control and Drainage Research was established in 1974 and later renamed as the Institute of Water and Flood Management (IWFM) in 2002. The Institute pursues research and capacity development in the field of water and flood. management that is vital for economic development and social prosperity of the country. The Institute also provides advisory and consultancy services to government and non-government organizations. Please see here for more about the institute.
[detail] --> |
|
 |
Department of Disaster Science and Management (DSM)
|
| Outline According to the Centre for Research on the Epidemiology of Disasters (CRED), 336 natural disasters and 234 technological disasters were reported worldwide in 2011 only. One trillion dollars have been lost in the last decade due to disasters and one million people killed. Disasters directly affect business performance and undermine longer-term competitiveness and sustainability........ The geographical location, land characteristics, multiplicity of rivers and the monsoon climate render Bangladesh highly vulnerable to natural hazards. The coastal morphology of Bangladesh influences the impact of natural hazards on the area. Particularly in the southwestern area, natural hazards increase the vulnerability of the coastal dwellers and slow down the social and economic development. Moreover, climate change and human induced hazards add a new dimension to community risk and vulnerability. Humanitarian implementation plan (2012) shows that Bangladesh loss about 6188 lives and have to suffer 550 $ million economic loss due to only natural disasters. Global Assessment Report (2011) published by UNISDR reveals that Bangladesh is in 1st and 6th position in terms of vulnerability of flood and cyclone respectively. Recently GERMANWATCH shows that Bangladesh is in 2nd position in Climate Change Vulnerability Index. So it has no denying that our motherland is in a great risk of disasters. As of late, the world is giving more emphasize on disaster risk reduction through strengthening preparedness and mitigation measures over response and recovery activities. This is known as paradigm shift. There exists a saying if we spend 1$ for disaster risk reduction we can save 10 $ equivalent cost in during and post disaster situation. So Bangladesh is also giving more concentration to make the nation resilient through disaster risk reduction, climate change adaptation and sustainable development.
Bangladesh is world renowned for disaster management. Its main reason is the development of capacities among people through living with disasters over years and already developed indigenous knowledge. But if we can integrate science based knowledge with existing endowed knowledge the comprehensive disaster management system will be more effective and fruitful. To fulfill this goal, Dhaka University, the highest echelon of academic excellence in Bangladesh, established a new department named Disaster Science and Management (DSM) under the Faculty of Earth and Environmental Sciences in 2012. The main objective of this department is to represent it worldwide as a research hub in the field of both hazard science and disaster management.
Newly established DSM maintains a vibrant academic environment encompassing a rich library with good collections and two laboratories. All the computers are installed by licensed ArcGIS and Erdas Imagine software in Geo-Information Lab. This lab has the facilities of interpretation of aerial photos and some multihazard risk assessment software as well. The Geophysical and Geo-technical Hazard Risk Assessment Labs are equipped with most efficient equipment like PS logging, 48-channel Seismometer, Microtremor Instruments, Consolidation (Oedometer), Direct Shear Test instrument, Total Station etc. While all teachers and students can use the broadband and Wi Fi Internet facilities, the department uses Multimedia Projector in the classrooms and in laboratorie [detail] --> |
|
 |
Federal University of Campina GrandeCampina Grande |
| Outline The Federal University of Campina Grande (UFCG) is located in the State of Paraíba, in the north-eastern region of Brazil. UFCG is a multi-campi university, with campuses in 7 cities of the state, with 11 academic centres, 1,481 faculty members, 1,420 staff members, 19,000 undergraduate students, 1,800 graduated students and 250 research groups in many different fields of expertise: Agrarian Sciences; Biological Sciences; Health Sciences; Exact Sciences and Earth; Humanities; Social Sciences; Engineering; Literature and Arts. The university´s research focuses on studies and research on environmental disasters in a broad sense, spanning several areas. This is partly motivated by the institution's location in the semiarid region of Brazil, high populated and socially and economically vulnerable to environmental hazards, such as droughts, desertification, land degradation, flash floods, health vulnerability, leading to social inequality. Research challenges addressed by our research groups are strongly related to, among other topics, water availability, pollution, access and management, epidemics of dengue, Zika virus and Chikungunya, resilient agroecology and family-based agriculture, climate variability and change, waste management, regional sustainability, disaster monitoring in rural and urban environments, risk communication, land cover and change, desertification. [detail] --> |
|